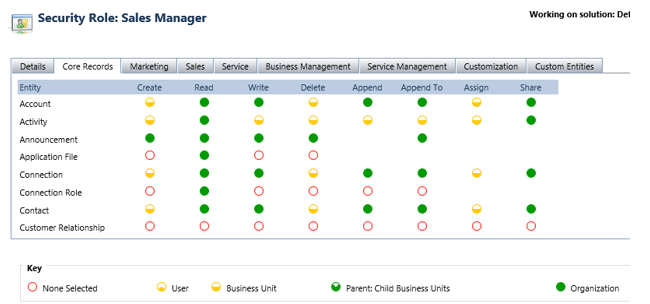
Role-based security – In Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2015 and Microsoft Dynamics 365 (online) the fundamental concept in role-based security is that a role contains privileges that define a set of actions that can be performed within the organization. Roles are grouped under different tabs based on their functionality. These groups include: Core Records, Marketing, Sales, Service, Business Management, Service Management, Customization and Custom Entities.

Terminologies:
Roles: Microsoft Dynamics 365 includes fourteen predefined roles that reflect common user roles with access levels defined to match the security best-practice goal of providing access to the minimum amount of business data required for the job. Also it is possible to add custom roles.
Privileges: A privilege authorizes the user to perform a specific action on a specific entity type. Each role defines a set of privileges that determines the user or team’s access to information within the company. It is not possible to add or remove privileges, or change how privileges are used to grant access to certain functionality, but it is possible to construct new roles from the existing privilege set.
Access levels: The access level or privilege depth for a privilege determines, for a given entity type, at which levels within the organization hierarchy a user can act on that type of entity. Levels of access in Microsoft Dynamics 365 are:
1. None: No privileges are given.
2. User: Privileges to the records owned by the user or shared with the user. Also includes the privileges owned by the team to which the user belongs.
3. Business Unit: Privileges for all records owned in the business unit to which the user belongs.
4. Parent: Child Business Unit: Privileges for all records owned in the business unit to which the user belongs and to all the child business units subordinate to that business unit.
5. Organization: Privileges for all records in the organization regardless of who owns it
Create a security role:
1. System Administrator or System Customizer security role or equivalent permissions are required.
2. Go to Settings > Security.
3. Click Security Roles.
4. On the Actions toolbar, click New.
5. Set the privileges on each tab.
6. Click Save and Close.
Edit a security role:
1. System Administrator or System Customizer security role or equivalent permissions are required.
2. Go to Settings > Security.
3. Click Security Roles.
4. In the list of security roles, double-click or tap a name to open the page associated with that security role.
5. Set the privileges on each tab.
6. Click Save and Close.
Copy a security role:
1. System Administrator or System Customizer security role or equivalent permissions are required.
2. Go to Settings > Security.
3. Click Security Roles.
4. In the list of security roles, under Name, click or tap to select the security role you want to copy, and then on the Actions toolbar, click or tap More Actions > Copy Role.
5. In the Copy Security Role dialog box, in the New Role Name text box, type in the name for the new security role.
6. To modify the new security role after creating a copy, verify that the Open the new security role when copying is complete check box is selected; otherwise, clear the check box.
7. Click OK.